Bypassing WAFs Using Oversized Requests
by Alan Buxbaum (Guest Author) || Collaborator Jeff Barbi
Alan Buxbaum is a penetration tester based in Japan. His interest in blockchain technology and cryptocurrency led him to infosec where he’s worked professionally since 2025. In his free time, he is an avid Ashtanga yoga practitioner and musician.

TL;DR
Many web application firewalls (WAFs) can be bypassed by simply sending large amounts of extra data in the request body along with your payload. Most WAFs will only process requests up to a certain size limit. How the WAF is configured to handle these large requests determines exploitability, but some common WAFs will allow it by default.
A Bit about WAFs…
During a penetration test, it can be frustrating when a vulnerability exists in the app itself but payloads are blocked by a WAF, thereby preventing exploitation. This is not an uncommon scenario, especially in white or gray box testing where server-side code is available.
In such cases, WAFs can often be bypassed with payload obfuscation or other evasion techniques, indicating a gap in the ruleset or how it’s applied. Many great resources exist on this topic, such as this section of the Awesome-WAF repo from 0xInfection. Our research explores one such evasion technique we’re calling “oversized request bypass.”
WAF Limitations and You
Since inspecting large requests requires more processing time and resources, many WAFs have a limit (often configurable) on the max size request it will process. What a WAF does with requests above this size limit is an important consideration — not just for security, but also app functionality.
Some apps generate very large requests from users during normal use. For these apps, it’s important that a WAF not cause denial of service issues by blocking large but legitimate requests. Our research investigates how different WAFs approach this issue, and shows how you can take advantage of these configurations during a pentest.
A Simple Example
Consider a web application example.com that’s fronted by a WAF using an OWASP-based ruleset. The app has an SQLi vulnerability in the username parameter of the homepage.
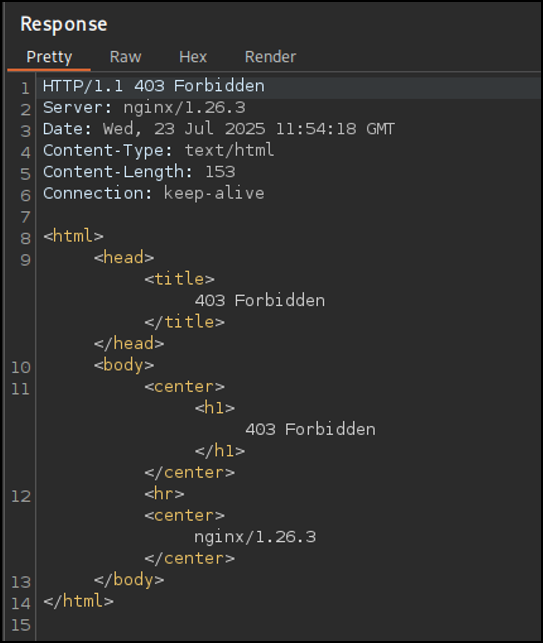
An attacker sends a request with a malicious payload. The WAF inspects the request and rejects it with a 403 Forbidden:
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Length: 47
username=foo'+OR+1=1;--&password=B3$tP@ssw0rd3v3r
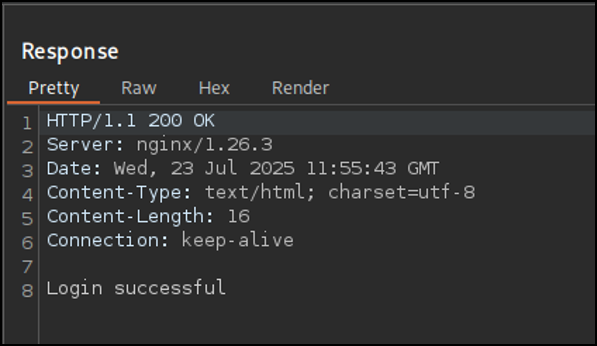
However, the attacker learns that this particular WAF’s request size limit is 8172 bytes. They prepend an extra POST body parameter foo with 8172 characters, just enough to exceed the WAF’s size limit. As a result, the body content is ignored and the payload is passed on to the application:
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Length: 8249
foo=8172_CHARS_HERE&username=foo'+OR+1=1;--+-&password=B3$tP@ssw0rd3v3r
Our Goal
Our research goal was to test and document the default behavior of common WAFs when presented with the above situation. To do this, we made a simple Flask app with an SQLi vulnerability in the username and password parameters of its login form. We then tested each WAF by putting the application behind them and seeing how they fared against an oversized request bypass attack.
Before We Begin…
Since a WAF developer cannot know the nature of the application their product will one day protect, WAFs are designed to be very flexible. As a result, the “insecure” settings mentioned above generally arise from the impossible task of balancing security with functionality.
We want to make it clear that the purpose of this writeup is to shed light on these tradeoffs, rather than blaming WAF designers and/or their design choices.
Cloudflare
Product link: Cloudflare WAF
Documentation: Cloudflare WAF Documentation
Bypassable by Default?
Yes. For free accounts, requests with 8216 or more bytes prepended to a payload will bypass the WAF. These sizes may vary depending on which account is being used (see below for more details).
Details
Cloudflare addresses oversize request handling directly in their docs here:
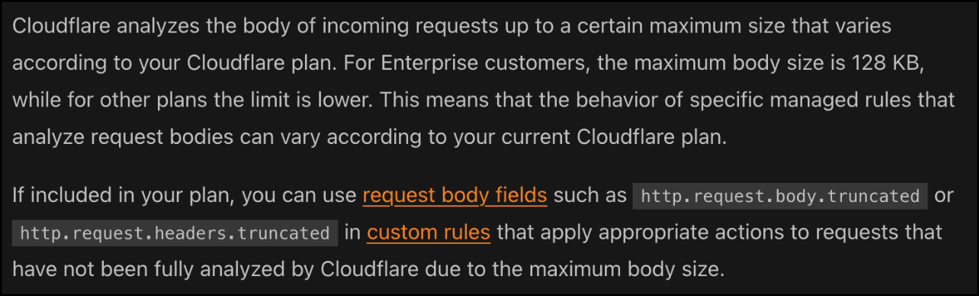
As seen above, enterprise-tier customers have a maximum body size limit of 128 KB. This is significantly larger than the free-tiered plan, which is about 8 KB.
Hardening Tips
In order to customize how Cloudflare’s WAF handles oversize requests, enterprise customers have access to configure request body fields such as http.request.body.truncated and http.request.headers.truncated.
For free-tiered customers, any POST body over the 8 KB size limit will be sent through.
Barracuda
Product link: Barracuda WAF (tested with AWS Marketplace Trial)
Documentation: Barracuda WAF Documentation
Bypassable by Default?
No.
Details
Barracuda’s WAF does not implement size limits on POST body requests by default. As a result, there is no size delta for an attacker to insert a payload.
However, size limits can be implemented (as seen per the documentation below):

Hardening Tips
Make sure to turn Active mode on.
ModSecurity
Product link: ModSecurity Github
Documentation: ModSecurity Documentation
Bypassable by Default?
Yes. ModSecurity starts off in detection mode (SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly) and with SecRequestBodyLimitAction set to Reject. While the latter parameter is the secure setting, it won’t have any effect due to SecRuleEngine being set to DetectionOnly.
Once SecRuleEngine is changed to On, setting SecRequestBodyLimitAction to ProcessPartial is insecure:
SecRuleEngine On
SecRequestBodyAccess On
SecRequestBodyLimit x
SecRequestBodyLimitAction ProcessPartialCharacters after x number of bytes will bypass the WAF.
Details
As referenced above, ModSecurity’s configuration file starts off with SecRequestBodyLimit set to 13107200 and SecRequestBodyLimitAction set to Reject. This means that any request with a body size over 13 MB will be rejected.
Hardening Tips
Set SecRequestBodyLimitAction to Reject, so that for SecRequestBodyLimit x, ModSecurity will block any request over x size.
AWS
Product link: AWS WAF
Documentation: AWS WAF Documentation

Bypassable by Default?
Yes. Insecure with a request body size of more than 8KB by default when used in conjunction with the Application Load Balancer. Sizes vary depending on the service (see below for more details).
Details
AWS explicitly discusses risks re: oversized payloads here. Specifically:
Body and JSON Body – For Application Load Balancer and AWS AppSync, AWS WAF can inspect the first 8 KB of the body of a request. For CloudFront, API Gateway, Amazon Cognito, App Runner, and Verified Access, by default, AWS WAF can inspect the first 16 KB, and you can increase the limit up to 64 KB in your web ACL configuration. For more information, see Managing body inspection size limits for AWS WAF.
AWS also discusses size limits of different services here:
For CloudFront, API Gateway, Amazon Cognito, App Runner, and Verified Access, the default limit is 16 KB (16,384 bytes), and you can increase the limit for any of the resource types by increments of 16 KB, up to 64 KB. The setting options are 16 KB, 32 KB, 48 KB, and 64 KB.
Hardening Tips
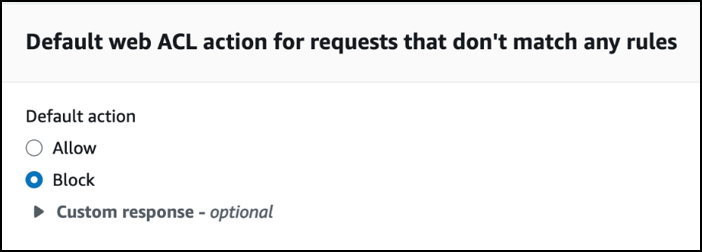
During deployment, set the “Default web ACL action for requests that don’t match any rules” to “Block”.
Azure (Application Gateway)
Product link: Azure WAF
Documentation: Azure WAF Documentation; Azure WAF on Application Gateway
Bypassable by Default?
No. Not insecure in any configuration due to “fail closed” design in prevention mode.
Details
Due to Application Gateway WAF’s “fail closed” design, any request body that’s over the size limit will not get passed on to the application (details on this can be found here).
Regardless, you can still set the Application Gateway WAF to various limit sizes via its configuration:
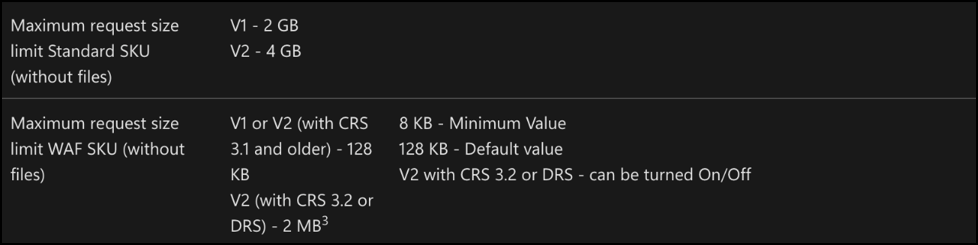
Hardening Tips
N/A
Azure (Front Door)
Product link: Azure WAF
Documentation: Azure WAF Documentation; Azure WAF on Front Door
Bypassable by Default?
Yes. AFD defaults to a request body size limit of 128KB. Additionally, the WAF defaults to Detection mode and must be changed to Prevention mode in order to block requests under the size limit.
Details
Azure policy recently changed from requiring a Premium license to use managed rule sets. As of 2025, this functionality is included with Standard as well.
Hardening Tips
As stated in Azure’s Best Policies, make sure to switch to Prevention mode.
Google Cloud Armor
Product link: Google Cloud Armor
Documentation: Google Cloud Armor Documentation
Bypassable by Default?
Yes. Google Cloud Armor’s default settings include an 8 KB character size limit.
Details
Set up is a bit more involved than others and can be found here. In order to use preconfigured rulesets, the WAF must be set to advanced mode.
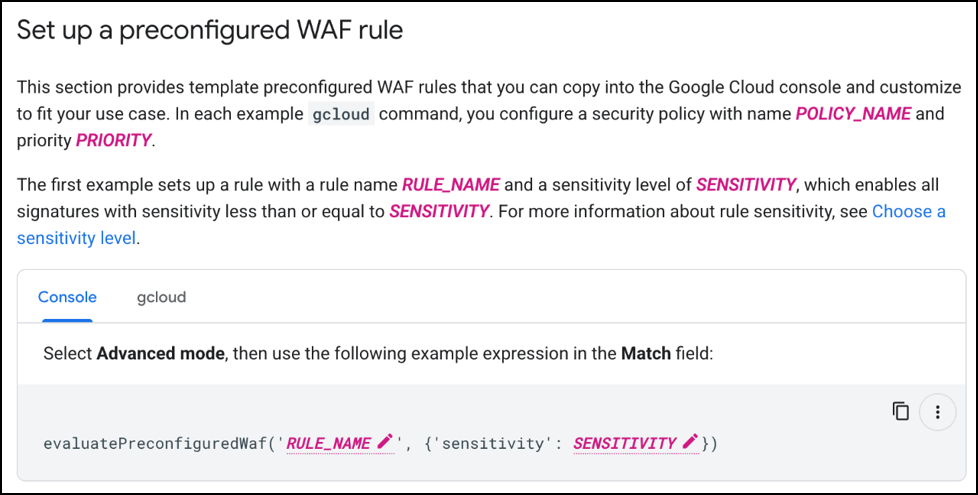
Hardening Tips
Google Cloud Armor can be set to filter and block requests over a specific size. This can be found under Cloud Armor Policies > [Name of Policy] > Edit Rule.
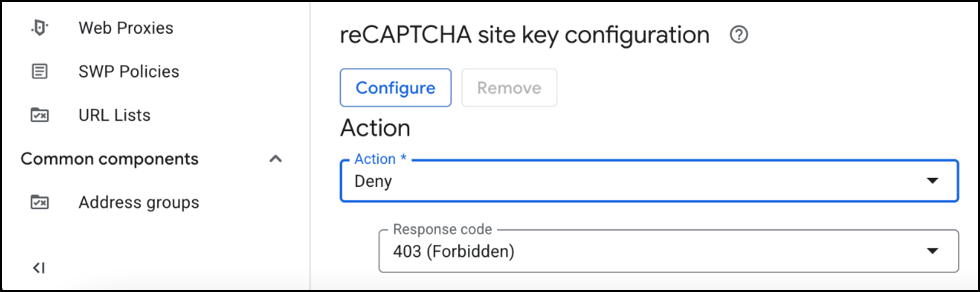
Riyaz Waliker’s article discusses options for extenuating circumstances:
…further conditions could be added along with the Content-Length check to finely tune when Cloud Armor filters and blocks requests. For instance, a rule that would allow requests larger than 8 KB only for a specific endpoint could be added to the security policy targeting a given application.
You can find more information about various allow/block configurations here.
Sucuri
Product link: Sucuri WAF
Documentation: Sucuri WAF Documentation
Bypassable by Default?
Yes. Sucuri’s WAF defaults to 1.25 MB.
Details
Security Level must be set to “High” to allow POST requests. When set to “Paranoid”, POST requests are not let through.
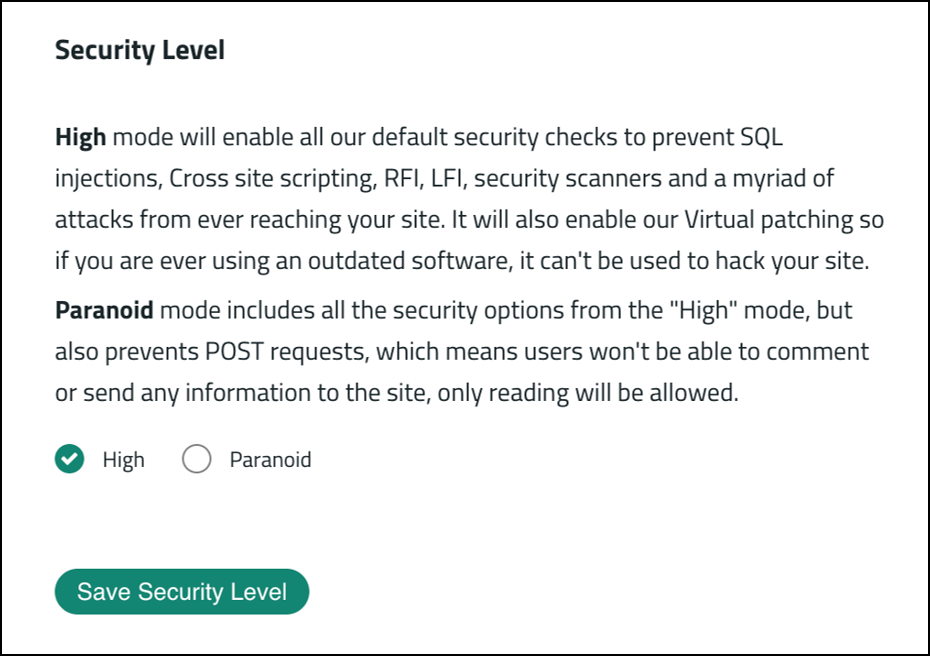
Specifics on Sucuri’s character size limit are neither in the documentation nor configurable from the user’s GUI.
It should be noted that Sucuri’s WAF default rules did not block the payload we used to test the others WAFs ‘ OR ‘1’=’1′;– so we used ‘ UNION SELECT 1,2,3;– which was blocked.
Hardening Tips
N/A
Fortinet
Product link: Fortinet FortiWeb WAF (tested with Azure Trial)
Documentation: Fortinet FortiWeb Documentation
Bypassable by Default?
Yes. Fortinet’s character size limit is 64 MB.
Details
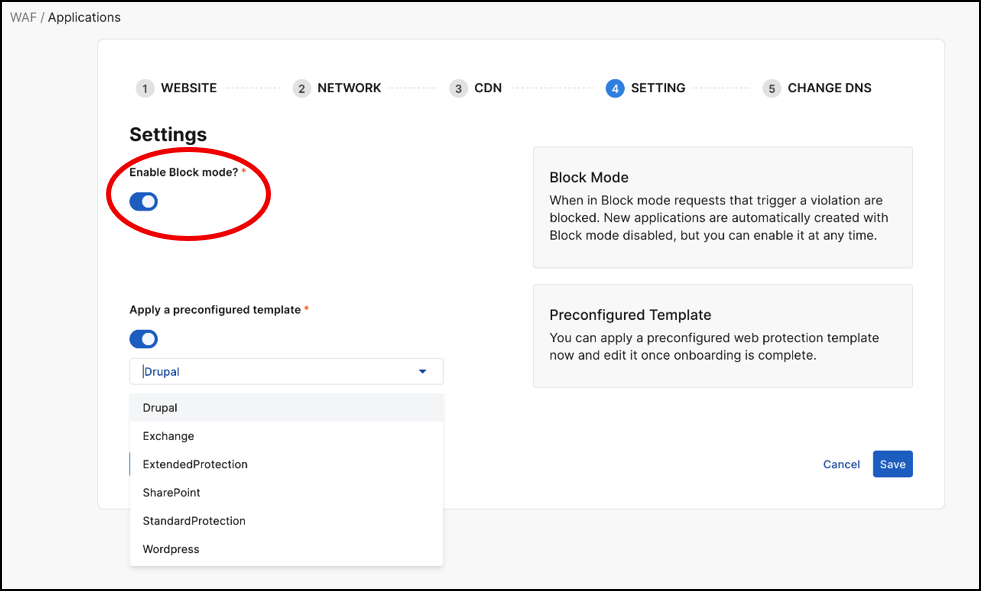
Fortinet’s WAF defaults to “Block mode” being off.
Hardening Tips
In “Settings”, enable “Block mode”:
In addition, various sensitivity levels can be set that control FortiWeb WAF’s behavior (as seen here).
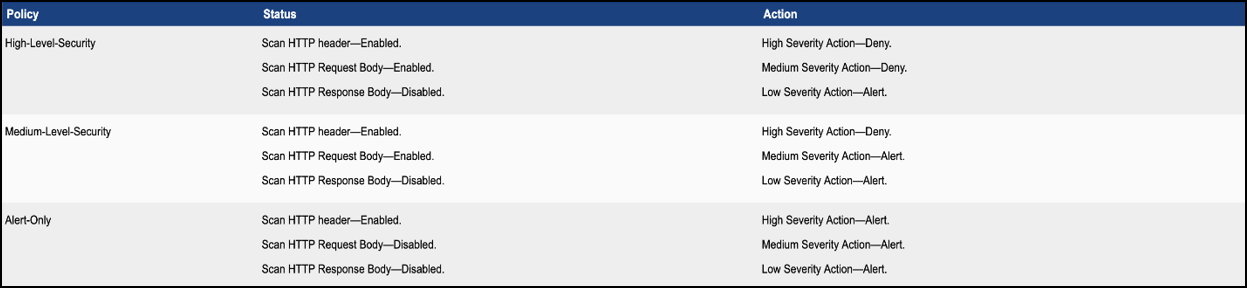
You can find more details on FortiWeb’s default settings here.
Conclusion
Oversized requests reveal a fundamental tension in WAF design: balancing performance, usability, and security. Our findings underscore the importance of testing WAFs – not just for rule coverage, but for how they handle scale and resource limits.
Security defaults matter, but so does understanding how they interact with real-world application behavior. Ultimately, the responsibility to close these gaps lies with both defenders and the tools they configure.
Ready to learn more?
Level up your skills with affordable classes from Antisyphon!
Pay-Forward-What-You-Can Training
Available live/virtual and on-demand

